Dietary Copper Interactions: Protagonists, Antagonists and Heavy Metal Accumulation

Dietary Copper Interactions in Pigs
Mineral interactions are complicated and not very well understood. A nutritionist has to consider the concentration and form (organic, inorganic, sulfate, oxide, etc.) of a supplemented mineral. They also have to consider the concentration of the minerals that are not supplemented. And, they have to expect different types of interactions in different organs.
Aldridge et al explored how feeding copper in different concentrations and forms altered the status of other minerals in organs of weanling pigs. They conducted a 14-day feeding trial with pigs fed Cu sulfate or Bioplex Cu at 0, 4, 25 or 125 ppm Cu. They measured accumulation of several minerals in intestinal tissue, liver, gall bladder and serum.
Some of their findings?
- Copper as Antagonist: As Cu increased in the diet, Se, Mo, Mg and Zn declined in various organs.
- Copper as Protagonist: When Cu was fed at 125 ppm increased levels were seen for Co and Mn in the kidney; Co in serum; and Fe in the intestine.
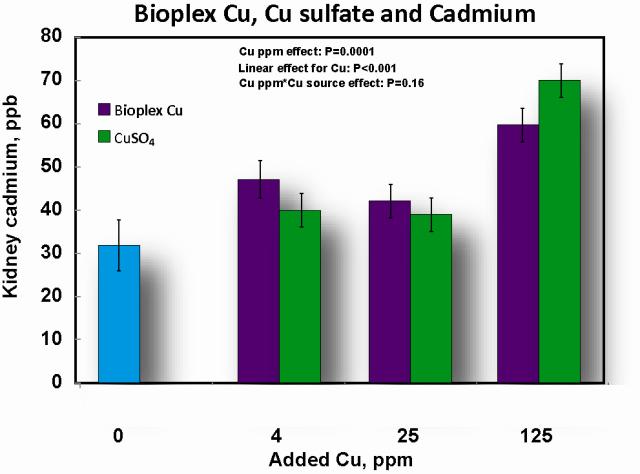
- Copper and heavy metal accumulation
- As dietary Cu increased, so did liver lead and Cd with more of each accumulating from CuSO4 compared with Bioplex Cu.
- Cd accumulation in the kidney was highest at 125 ppm Cu; the increase was 16% greater for pigs fed CuSO4.
- Serum Se, Mo: Overall, when pigs were fed Bioplex Cu, more serum Se and Mo was present in blood serum.
The authors concluded that mineral interaction relationships cannot be generalized dietary forms, levels and target organs differ. They stressed the importance of considering interactions when requirements are set; and underlined the impact of Cu level and form on heavy metal accumulation.
The paper is being presented today at the 2011 JAM ( joint annual meeting) of the American Dairy Science Association (ADSA) and the American Society of Animal Science (ASAS).
Titles, authors, links:
All Categories
Archives
- 五月 2014 (6)
- 二月 2014 (1)
- 八月 2013 (1)
- 七月 2013 (1)
- 六月 2013 (4)
- 五月 2013 (17)
- 九月 2012 (1)
- 八月 2012 (22)
- 七月 2012 (1)
- 五月 2012 (24)
- 四月 2012 (2)
- 三月 2012 (12)
- 一月 2012 (7)
- 十二月 2011 (10)
- 十一月 2011 (12)
- 十月 2011 (2)
- 九月 2011 (4)
- 八月 2011 (12)
- 七月 2011 (10)
- 六月 2011 (11)
- 五月 2011 (35)
- 四月 2011 (4)
- 三月 2011 (10)
- 二月 2011 (12)
- 一月 2011 (13)







